Event driven architecture(EDA) is a more adopted nowadays as the whole event driven architecture based applications are only computed/triggers a business logic when a certain event or series of event occurs and also it decouples the monolithic application. In a event driven architecture will get all the feasibility to do multiple triggers and the trigger's business logic.
Event-driven architecture (EDA) is a software architecture paradigm promoting the production, detection, consumption of, and reaction to events. - Wikipedia
What makes Event-driven architecture more adopted v/s traditional architecture?
- EDA will only execute when the event is triggered and the callback/response may invoke another event trigger rather than execute the business logic itself, but the traditional systems would have to poll the to check if the previous/subsequent process is completed (if completed, successfully completed or not).
- When it comes to cost efficiency, EDA are more effective as with any cloud provider - AWS, GCP, Azure we would only pay for the resources when we use and for the duration we use them. With EDA, the resources are only triggered when the event occurs making it a "on demand" execution. But with traditional architecture, we would have the resources running but in idle state and of-course anything we run irrespective of the state it is in, we would have to pay for it.
When to choose EDA over traditional architectures?
When to adopt an Event-driven architecture? We must always keep in mind EDA will not fit into all the use-cases, there would be scenarios when we will feel we are just overloading a event-driven application and its too much of wait time for the end-user to see the changes reflecting but also some use-cases would definitely need event based actions.
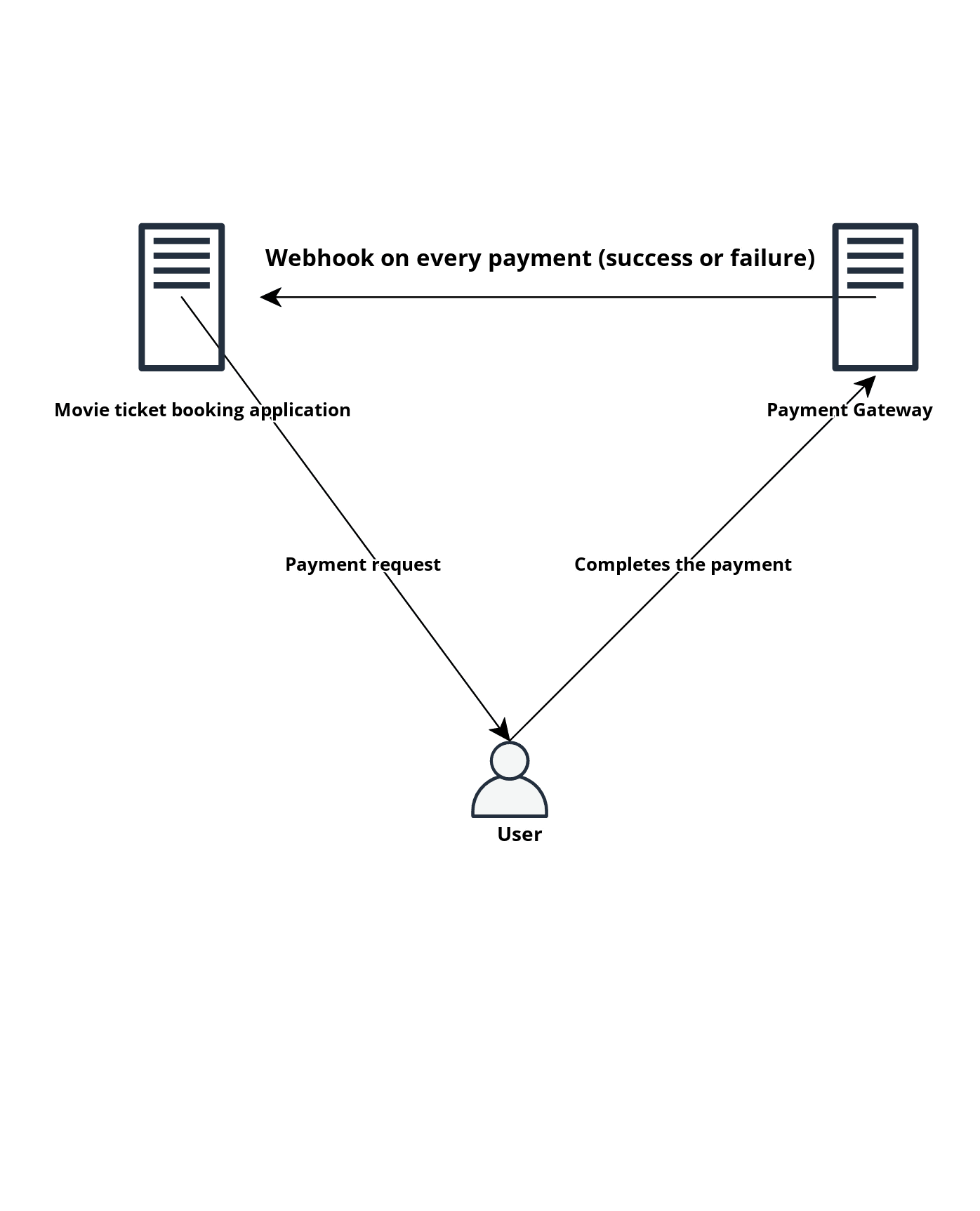
For example, a Movie ticket booking application, we can book a show for a set of seats and the application would internally wait for the billing to complete which on the success would grant you the tickets. This is where we see a event (successful payment) which the payment gateways would invoke via a webhook to the application's backend. If we don't have the webhook (a callback API which notifies with certain events) then, the ticket booking application would have to keep polling the payment gateway to check if the payment has been completed successfully or not. This is not only hit the performance of ticket booking application but also it will throttle the payment gateway's APIs as we would be polling in every x seconds.
Common use-cases which involves EDA
Publisher-subscriber models such as IoT based architecture, messaging platforms, streaming platforms.
E-commerce applications
Micro-services architecture

