AWS AppSync has been one of the powerful integration service for Front-end and AWS serverless backend. The modern day applications which are developed in domains such as Chat, IoT, Mobile apps, Web apps choose AppSync over AWS API Gateway.
What is AWS AppSync?
AWS AppSync is a fully managed GraphQL API which is a serverless offering by AWS.
AWS AppSync is a fully managed service that makes it easy to develop GraphQL APIs by handling the heavy lifting of securely connecting to data sources like AWS DynamoDB, Lambda, and more. Adding caches to improve performance, subscriptions to support real-time updates, and client-side data stores that keep off-line clients in sync are just as easy. Once deployed, AWS AppSync automatically scales your GraphQL API execution engine up and down to meet API request volumes.
How AppSync works?
As mentioned AppSync is a serverless GraphQL offering by AWS, the underlying API uses GraphQL schema for the definition of the data models and the various other operations (such as queries, mutations, subscription).
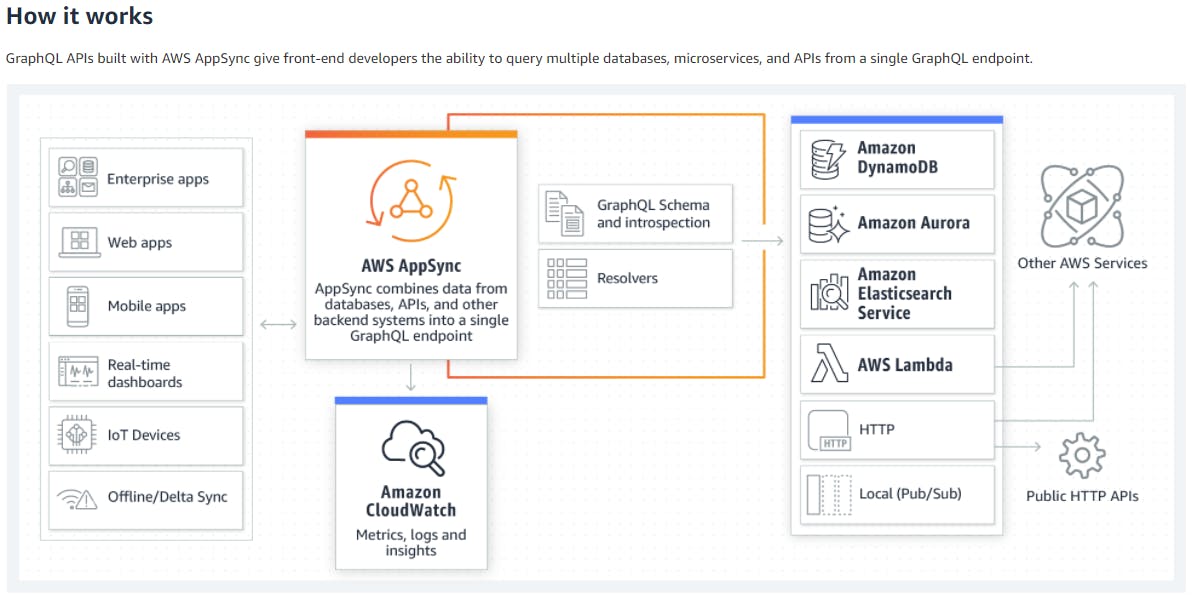
Every model or the operation would have a resolver with one of the defined data source, the resolver is the integration logic which is written in Apache Velocity Template Language (VTL) which is powerful to invoke and also perform actions on different AWS services and also HTTP APIs. And the resolver will also return the response back to AppSync. Resolvers not limited only to GraphQL actions such as queries, mutations and subscriptions but they can be added to various other model objects.
Key concepts to know before getting started with AppSync
GraphQL schema
Data source
Resolvers
GraphQL schema
Schema of the API which defines the data models, response objects, input objects and the actions types - queries, mutations and subscription.
Query - Any get or fetch operation from the database.
Mutation - Any data modifications or creations to the database.
Subscription - Listening to any real-time change in the data.
Schema example which was generated with sample project - Tasks App
type Mutation {
# In this example, only users in the ManagerGroup can create tasks
createTask(
owner: String!,
title: String!,
taskStatus: String!,
description: String!
): Task
@aws_auth(cognito_groups: ["ManagerGroup"])
# Both Employees and Managers can update a task's status
updateTaskStatus(id: ID!, taskStatus: String!): Task
@aws_auth(cognito_groups: ["EmployeeGroup","ManagerGroup"])
updateTaskBody(id: ID!, title: String!, description: String!): Task
@aws_auth(cognito_groups: ["ManagerGroup"])
}
type Query {
# Users belonging to both EmployeesGroup and ManagerGroup can read a particular task
getTask(id: ID!): Task
@aws_auth(cognito_groups: ["EmployeeGroup","ManagerGroup"])
# Only Managers can list all the Tasks
allTasks(nextToken: String): TaskConnection
@aws_auth(cognito_groups: ["ManagerGroup"])
}
type Task {
id: ID!
owner: String!
title: String!
description: String!
taskStatus: String
}
type TaskConnection {
items: [Task]
nextToken: String
}
schema {
query: Query
mutation: Mutation
}
Data sources
Data sources in context of AppSync are the seemlessly integrated AWS services and also a public HTTP endpoint. Whenever a data source is created for an AppSync API, an IAM role gets created in the background which provides invocation / read / write / list access to the AWS resource.
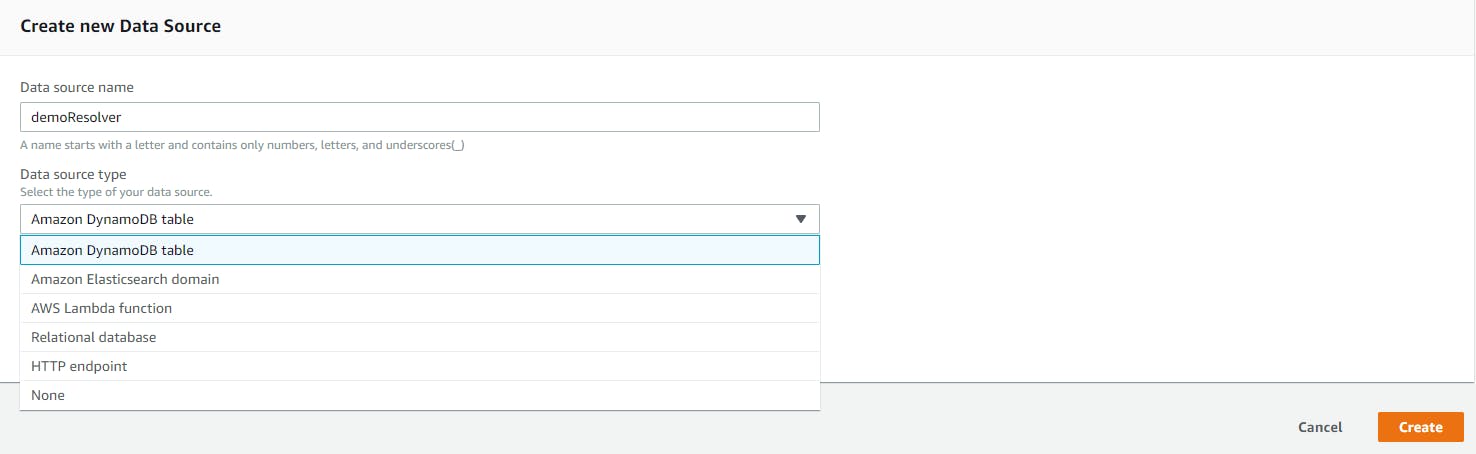
Different data sources supported on AppSync are -
DynamoDB table
Lambda function
Elasticsearch domain
Relational database (Aurora)
HTTP endpoint
Resolvers
Resolvers are the middleware which gets GraphQL schema and the data-source. Resolvers are written in Apache Velocity Template Language (VTL), these integrate seemlessly with data sources and also provides sample snippet to perform specific operations.
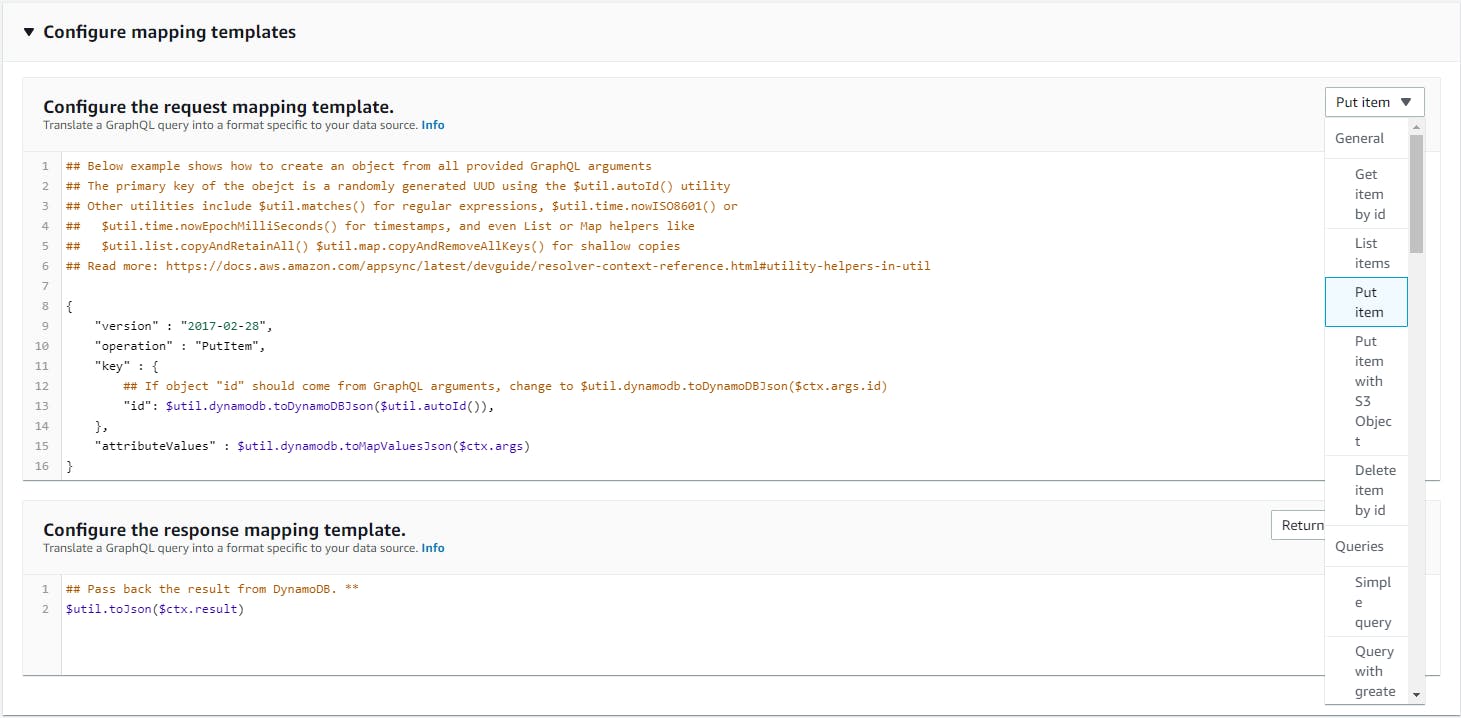
When data source is DynamoDB, AppSync console provides snippet for various operations such as GetItem, ListItems, PutItem, Query with filters, and many more other DynamoDB operations. Different resolvers on AppSync -
Unit resolvers - Direct resolvers to the data source.
Pipeline resolvers - Multiple resolvers which are defined as functions to do multiple processing with multiple data sources.
Authorization on AppSync
AppSync APIs have to be authenticated to make the APIs more secure. AppSync API by default is authenticated with API Key which is valid for 7 days and could be extended upto 365 days. AppSync supports various authentication methods -
AWS IAM - IAM role which could be used from backend (AWS Lambda fn) and also which can be assigned to the Identity from Cognito Identity Pool.
API Key - API key which gets created from the AppSync API setting.
AWS Cognito User Pool - Authenticated user of the Cognito User Pool would have access to invoke AppSync's queries, mutations, subscriptions. This is achieved with access tokens retrieved from Cognito sign-in.
OpenID Connect - The custom authorizers supported with OpenID Connect provider.
AppSync doesn't restrict to only one authorization method per API but facilitates multiple authorizations with one of the authorizer set as default. When using multiple authorization methods, the different type objects, queries, mutations, subscription can be restricted to specific authorized method only with the authentication directives @aws_api_key, @aws_iam, @aws_cognito_user_pools and @aws_oidc.
type Task @aws_cognito_user_pools{
id: ID!
owner: String!
title: String!
description: String!
taskStatus: String
}
Additionally, @aws_auth could be used with @aws_cognito_user_pools to provide fine-grain access to users who belong to specific User Groups defined in the Cognito User Pool.
type Query {
# Users belonging to both EmployeesGroup and ManagerGroup can read a particular task
getTask(id: ID!): Task
@aws_auth(cognito_groups: ["EmployeeGroup","ManagerGroup"])
# Only Managers can list all the Tasks
allTasks(nextToken: String): TaskConnection
@aws_auth(cognito_groups: ["ManagerGroup"])
}
getTask(id: ID!) query can be invoked from the authenticated users who are part of EmployeeGroup and ManagerGroup whereas allTasks(nextToken: String) query can be invoked from authenticated uysers who are part of only ManagerGroup in Congito User Pool.
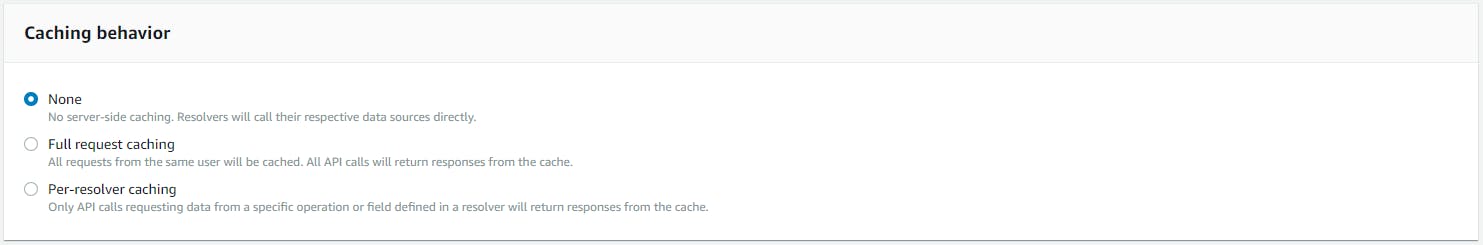
Caching
AppSync API has caching capabilities so that the client does not have always load the data from server so that the user experience is more enhanced.
Code integration for front-end developers
AppSync is offered under the AWS Amplify family, the AppSync API can be easily added to the front-end Amplify project with ease of Amplify CLI command amplify add codegen and amplify codegen. Adding AppSync API to front-end Amplify project.
$amplify add codegen --apiId xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Once the AppSync API is added, Amplify generates the AppSync configuration with the details such as API_endpoint, region, app_id, authentication method. From the added API, the complete schema can be generated in the language of the client (such as JavaScript, Java, Kotlin, Swift) with the respective files and classes for all the objects, queries, mutations, subscriptions.
$amplify codegen
This generates the respective files in your Amplify project. Any change in the AppSync schema can be easily reflected on the front-end project with the above Amplify CLI command.
AppSync limitations
AppSync is a great integration service, unfortunately this has certain limitations as well.
Max AppSync APIs (Soft limit) - Every AWS account has a soft limit of 25 APIs per region.
Throttling (Soft limit) - 1000 queries per API per second.
Schema size - GraphQL schema has a maximum document size of 1MB.
Subscriptions per user session - 100 active subscriptions are allowed per user session.
Execution timeout - 30 seconds of maximum execution timeout for a request.
AppSync service qouta provides a detailed information about AppSync limits and also the soft limits which can be increased by raising a support ticket.
Conclusion
AWS AppSync is a perfect choice for any modern day application - Mobile and Web and IoT based application which eases the integration and development with GraphQL serverless offering. And AWS Amplify takes it to another level for the developers to get-going!

